neighbor
cell optimization HUAWEI CDMA2000 NETWORK
OBJECTIVE
Optimize the
network on the basis of analysis collection PSMM trace data. These data it is
possible to receive, I use a command SET PSMMTRACE of the
controller.
This command is used
to start or stop the neighbor cell optimization data collection task of the
CDMA2000 1X system.
After the data collection task is
started, a specified number of calls are traced and specified messages such as
PSMM, PPSMM, EPSMM, or CFSRPT reported by these calls are collected, saved as a
text file, and then sent to the network Huawei optimization analyzing tool for
the neighbor cell optimization analysis.
This tool is a paid product and does not extend
freely. Therefore for the analysis of the information containing in a file
we have developed the special program. This program will transform a binary
file to a usual text file which is convenient for analyzing.
Huawei PSMM trace
viewer. v1.0 Copyright (c) 2008
File:
PSMMTRACE3.dat
Date: 2008-5-24
14:55:42.225
Version:
BSC6600-OMCV100R003ENGC03B118
EcIo: 12
Subscribers: 50 BTSID: 04 Chanel: 0200
CH:200 CID:42
S:76 CID:40 S:88
CH:200 CID:41
S:75 CID:1a1 S:88
CH:200 CID:10
S:95 CID:a1 S:86
CH:200 CID:50
S:100 CID:42 S:20
CH:200 CID:40
S:77 CID:41 S:11
CH:200 CID:50
S:93 CID:10 S:88
CH:200 CID:50
S:95 CID:10 S:24
CH:200 CID:41
S:74 CID:60 S:88
CH:200 CID:40
S:74 CID:41 S:24
CH:200 CID:40
S:73 CID:41 S:24
CH:200 CID:40
S:74 CID:1a2 S:86
CH:200 CID:41
S:77 CID:210 S:20 CID:200 S:88
CH:200 CID:41 S:71
CH:200 CID:42
S:74 CID:40 S:84
CH:200 CID:40
S:76 CID:1a1 S:20 CID:41 S:86
CH:200 CID:40
S:83 CID:41 S:14 CID:1a2 S:88
CH:200 CID:41
S:92 CID:21 S:22 CID:51 S:87
CH:200 CID:40
S:75 CID:1a1 S:24 CID:1a2 S:88
CH:200 CID:41
S:85 CID:210 S:13 CID:42 S:88
CH:200 CID:a1
S:77
CH:200 CID:42
S:87 CID:210 S:13 CID:41 S:23 CID:52 S:88
CH:200 CID:a0
S:88 CID:a2 S:24 CID:40 S:23 CID:1a2 S:88
On all
questions of use of this program write to cdmatest@yandex.ru
INTRODUCTION
Soft handoff – add to active set
Soft handoff is a complex process.
Mobile station supports handoff as it
moves from one area to another. Along the way, it transfers its communication
from one base station to another. There are different handoff scenarios in
different states of the mobile station.
Soft handoff occurs when the mobile begins
to communicate with the second base station without breaking its communication
path with the current serving base station. In general, this is known as the
“make before-break” approach. During the soft handoff, the mobile can
communicate with more than two base stations simultaneously. IS-2000.5-0
defines the maximum number of simultaneous links to be six, which implies that
the mobile can talk to six base stations at the same time. Each base station
has its unique pilot. The pilot provides the mobile stations with a timing
reference and the information for the mobile stations to acquire the
communication with the network. The pilots of the base stations that the mobile
is actively communicating over the traffic channel constitute the mobile’s active set. The mobile generally initiates soft handoffs. During
a call, when the mobile is in the mobile station control on the
traffic channel state , it will
continuously scan for better pilots. Better pilot refers to the pilot that has
a stronger signal strength than the add threshold (T_ADD). If better pilots are found, then the mobile
reports them to the base station. Thus, the mobile assist the base station in
soft handoff. This is characterized as the Mobile Assisted Handoff (MAHO)
approach.
In order to achieve soft handoff, the
participating base stations must support the same frequency. The mobile
transmits on the same frame offset on all communication links. In other words,
soft handoff can only be used between CDMA channels having identical frequency assignments.
As mentioned earlier, the mobile
maintains the links with multiple base stations during soft handoff. The mobile
stores the values for add threshold and drop threshold (T_DROP) for adding or dropping a base station during soft
handoff. These thresholds are supplied to the mobile at call initiation.
The mobile maintains a list, called
the active set, of the base
stations involved in soft handoff. It maintains a list of candidates, called candidate set, whose measured signal strength are above the add threshold. The mobile assists in soft handoff by reporting both
lists to the system whenever a new candidate appears in the candidate set or the signal strength of an existing base station in
the active set falls below the drop threshold. The system can add base stations from the candidate set to soft handoff or drop base stations during soft
handoff.
Pilot sets are groups of pilots.
Pilots are stored in different groups to assist the mobile in soft handoff.
Each mobile maintains its own pilot sets when it is on the traffic channel.
This set can be changed dynamically during a call by transitioning pilots among
different sets:
§ Active Set: Pilots (based stations) with which mobile is in soft
handoff. This active set can have up to
six pilots.
§ Candidate Set: Pilots not currently in the active set, but are candidates for handoffs. These pilots have been received by the
mobile with signal strength above the add threshold.
§ Neighbor Set: Pilots that are not currently in active or the candidate sets but are likely candidates for handoffs.
§ Remaining Set: All possible pilots in the current system excluding
pilots in neighbor set, the candidate set and the active set.
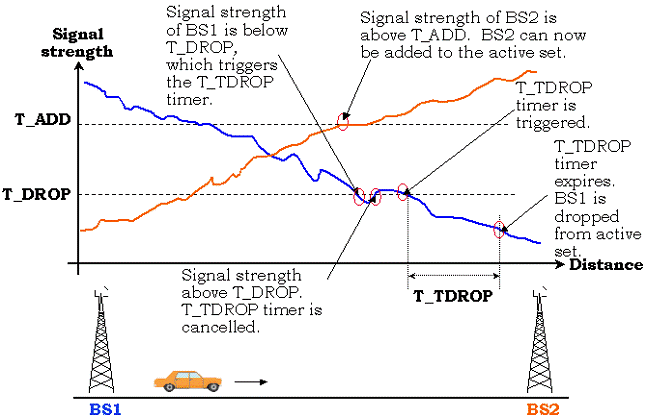
A
soft handoff scenario for a mobile station moving from BS1 to BS2.
Figure depicts the trigger for adding
and dropping a pilot. In this scenario, mobile starts moving from base station
1 (BS1) towards base station 2 (BS2). As it moves closer to BS2, the signal
strength of BS2 becomes stronger. Once the signal strength of this pilot
reaches the T_ADD threshold, this pilot can be added to the active set.
At the same time, the signal strength
of BS1 drops as the mobile moves away from BS1. Once the signal strength drops
below the T_DROP threshold, this event triggers the T_TDROP timer to be set. If
the signal strength goes above the T_DROP threshold before the T_TDROP timer
expires, the pilot will not be dropped. Only if the
signal strength is below the T_DROP threshold for at least the duration of the
T_TDROP timer, the pilot will be dropped from the active set.
1. As the mobile continuously scans for better pilots, it
detects the pilot for base station BS2. When the signal strength of the pilot
from BS2 rises above the add threshold, it then becomes a candidate for soft handoff. The
mobile sends a Pilot Strength Measurement Message (PSMM) to base station BS1. The PSMM includes both the
signal strength of the current serving pilots (active set) and potential candidates (candidate set).
2. Upon receiving the PSMM through BS1, the network
decides to add BS2 to soft handoff. After allocating internal resources in BS2
for the call, the network sends a Handoff Direction Message to the mobile through base station BS1. The Handoff Direction Message includes information about the set of traffic
channels, which includes BS1 and BS2. The BSC starts “multicasting” the forward
direction frames.
3. The mobile tunes to BS2 and sends a Handoff Completion Message to the network through BS1 and BS2. At this point, BS2
is added to soft handoff. The BSC starts “selection” of frames in the reverse
direction. The mobile starts “combining” frames in the forward direction.
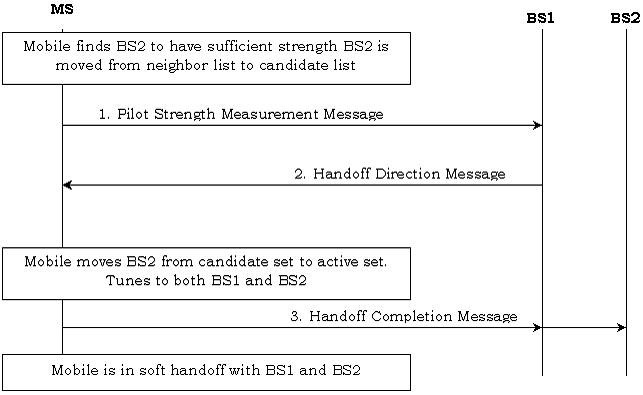
Message sequence
diagram showing pilot being added to the active set during soft handoff

OTA-R-FCH-pilot strength
measurement message for MS to return the pilot strength to BS, including pilots
in both active and candidate set.